Chapter-4: Microservices CI/CD with Azure DevOps
Azure DevOps Overview
Introduction:
Welcome to the fourth module of our series. In this module, we will look into fundamental concepts and establish a robust CI/CD pipeline using Azure DevOps. Specifically, we will explore Blue-Green deployment, Canary releases, and CI/CD strategies required for microservices on Kubernetes. Additionally, we will leverage tools like Helm and Argo CD. By the end of this module, you will have a clear understanding of how to create a comprehensive CI & CD pipeline architecture for deploying our Microservices into an AKS cluster.
Before we look into Azure DevOps CI & CD strategies, let's lay a solid foundation by revisiting some core DevOps concepts.
What is CI/CD?
CI/CD stands for Continuous Integration / Continuous Delivery (or Deployment). It is a set of practices and tools used in software development that aims to automate and streamline the process of building, testing, and deploying code changes to multiple environments like dev, test & production.
-
Continuous Integration (CI) - is the practice of frequently merging code changes from multiple developers or Teams into a central repository, verifying the changes through automated tests, and reporting any issues that arise. This helps to catch problems early on and ensures that the codebase remains stable and functional.
-
Continuous Delivery (CD) - is the practice of automating the entire software release process, from building the code to deploying it to production environments. This involves using tools and processes that enable the release of code changes quickly and reliably, while ensuring that the software remains stable and functional.
CI/CD helps to improve the speed and quality of software development, as well as reduce the risk of errors and downtime. By automating many of the processes involved in software development, teams can focus on creating value for customers rather than spending time on manual tasks.
In a microservices architecture, CI/CD refers to the automated process of building, testing, and deploying individual microservices.
CI/CD in microservices architecture helps to ensure that each Microservice is tested and validated before it is deployed, reducing the risk of bugs and errors in production. It also enables faster deployment cycles and more frequent updates, as each Microservice can be updated and deployed independently of the others. This approach makes it easier to scale and maintain complex applications, as individual microservices can be modified and updated without affecting the entire application.
Goals of a robust CI/CD process:
The goals of a robust CI/CD (Continuous Integration/Continuous Delivery) process include:
- Faster delivery of software: A robust CI/CD process should enable developers to deliver software faster, with automated processes for building, testing, and deploying code changes. This can help reduce the time to market for new features and bug fixes.
- Improved quality of software: Automated testing and validation help catch bugs and errors early in the development process, reducing the likelihood of issues in production. This leads to higher quality software that is more reliable and stable.
- Better collaboration among team members: CI/CD promotes collaboration among developers, testers, and operations teams, with automated feedback loops that help identify and resolve issues quickly.
- Greater efficiency in development: CI/CD automates many of the time-consuming and repetitive tasks involved in software development, freeing up developers to focus on creating new features and functionality.
- Increased agility in development: The ability to rapidly build, test, and deploy code changes enables developers to respond quickly to changing business requirements or customer needs.
- Lower costs: A robust CI/CD process can help reduce the costs associated with manual testing and deployment processes, as well as minimize the risk of downtime or other issues that can be costly for the organization.
A robust CI/CD process enables organizations to develop high-quality software faster and more efficiently, while also promoting collaboration and agility among development teams.
What is Blue-green deployment?
Blue-green deployment is a technique used in software deployment that enables organizations to deploy new versions of an application without downtime. In this deployment strategy, two identical production environments are created, and one environment is designated as the "blue" environment, while the other is designated as the "green" environment.
The current version of the application is running in the blue environment, and the new version is deployed to the green environment. Once the new version has been fully deployed and tested in the green environment, traffic is redirected from the blue environment to the green environment. This is done by switching the routing rules or updating DNS records.
At this point, the green environment becomes the production environment, while the blue environment is retained as a backup. Any issues with the new version can be easily addressed by reverting the routing rules back to the blue environment.
Blue-green deployment allows organizations to deploy new versions of an application with minimal risk and downtime. This strategy also enables organizations to test the new version of the application in a production-like environment, ensuring that any issues are identified and addressed before the new version is fully deployed.
Blue-green deployment is a powerful tool for software deployment that enables organizations to deploy new versions of their applications with confidence and speed, without risking downtime or disrupting the user experience.
What is Canary release?
Canary release is a deployment strategy that allows organizations to test new versions of an application in production, with a subset of users, before making it available to everyone. In a canary release, a small percentage of production traffic is redirected to the new version of the application, while the majority of traffic continues to use the current version.
Canary release enables organizations to test new features, performance improvements, or other changes in a production-like environment, without exposing all users to potential issues. By gradually increasing the percentage of traffic directed to the new version, organizations can carefully monitor the performance of the new version and quickly roll back if any issues arise.
This approach helps organizations to minimize the risk of deploying new versions of an application and ensure that the user experience remains stable and consistent. It also enables organizations to gather feedback from a small group of users before making changes available to everyone.
Canary release is a powerful tool for organizations to test and deploy new versions of their applications with minimal risk and disruption, while also enabling them to gather feedback and improve the user experience.
CI/CD strategy for microservices on Kubernetes
Deploying small scale applications to Kubernetes can be easily managed by creating deployment YAML manifest files but when it comes to hundreds of Microservices we need better tools and process for these kind of deployments, also one of our goals is to simplify the development, deployment, and scaling of complex applications and to bring the full power of Kubernetes to all projects. Azure DevOps pipeline provides a platform which allows all projects to develop, deploy and scale container-based applications, highly productive, yet flexible environment for developers.
The tools we are going to use to meet the goals are:
- Helm Charts
- ArgoCD
What Helm Charts?
One of the key tools we use from the Kubernetes ecosystem is Helm. Helm is a package manager for Kubernetes, which simplifies the process of installing and managing applications on a Kubernetes cluster. A Helm chart is a collection of files that define how an application should be installed and configured on a Kubernetes cluster.
What is Argo CD?
The second tool we are going to use for deploying our Microservices to AKS is ArgoCD. ArgoCD is a GitOps-based continuous delivery tool for Kubernetes. It is an open-source tool that allows you to declaratively manage and deploy applications on Kubernetes clusters.
We will talk more about these tools in the upcoming labs.
Deploying Helm Charts with Argo CD
The approach we will follow here involves deploying Helm Charts with Argo CD.
Argo CD provides flexible options for deploying resources using Helm charts. Helm charts are a convenient way to package, version, and deploy applications on Kubernetes. Here's how you can deploy Helm charts with Argo CD:
Argo CD allows you to deploy Helm charts directly from a Git repository. Here's how it works:
-
Repository Setup: First, ensure that your Helm chart is stored in a Git repository. This repository can be public or private, but Argo CD should have access to it.
-
Argo CD Configuration: In your Argo CD application configuration, specify the Git repository URL and the path to the Chart.yaml file. The Chart.yaml file is essential for Argo CD to understand how to deploy the chart.
-
Automatic Detection: When you sync your Argo CD application, it will automatically detect the Helm chart in the specified Git repository. Argo CD understands the structure of Helm charts and can render them during deployment.
-
Customization: You can customize the deployment by providing a values.yaml file or specifying values directly in the Argo CD application configuration. This allows you to tailor the Helm chart to your specific environment and requirements.
Deploying Helm charts with Argo CD provides a powerful way to manage complex Kubernetes applications. It simplifies the deployment process and allows for fine-grained customization to fit your specific needs.
Azure DevOps Pipeline
Azure DevOps Pipeline provides end-to-end CI/CD capabilities for building, testing, and deploying applications to various platforms, including Azure, AWS, and on-premises environments. It allows developers and DevOps teams to create, manage, and run automated build and release pipelines, and to integrate with various tools and services, such as GitHub, Jenkins, Docker, Kubernetes, and more.
Azure DevOps Pipeline provides a unified experience for continuous integration and continuous delivery, allowing teams to collaborate and automate the software delivery process, from source code management to production deployment. With Azure DevOps Pipeline, you can automate the building, testing, and deployment of your applications, enabling faster and more reliable releases.
Overall CI & CD Architecture
The following diagram shows our end-to-end CI/CD process for deploying Microservices in AKS.
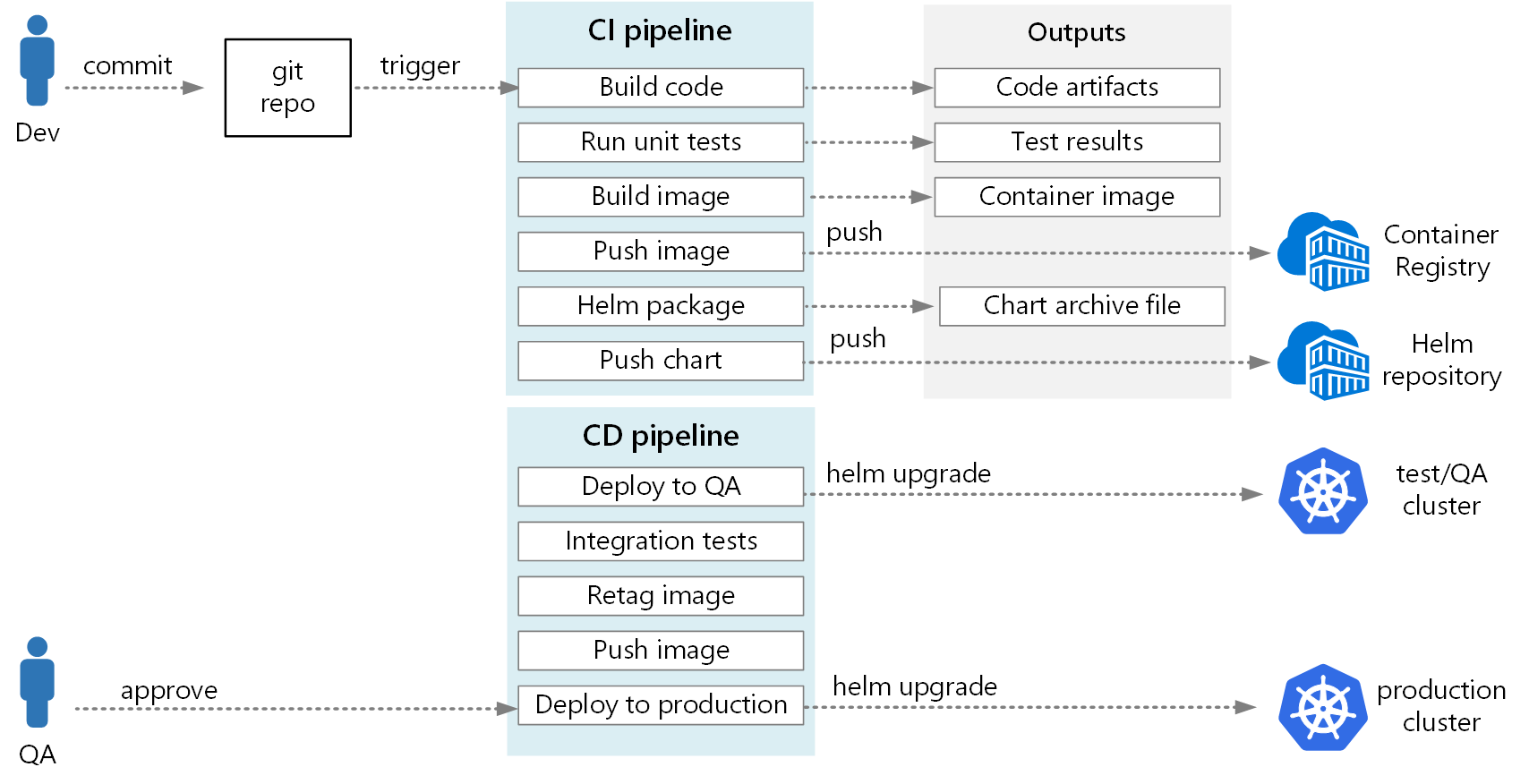
Reference Architecture diagram from MSDN documentation.
Reference
- https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/architecture/microservices/ci-cd-kubernetes - Build a CI/CD pipeline for microservices on Kubernetes with Azure DevOps and Helm